Equipment
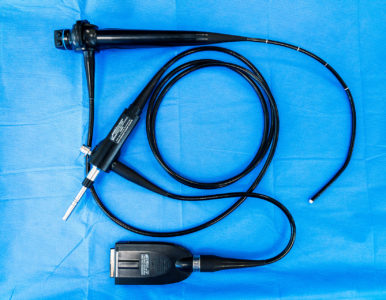
Flexible video ureteroscope Olympus URF V
The unit is only 3.3-mm- thick and flexible, which allows it to enter any part of the urinary system from the bladder to the farthest renal calyx. The URF-V videoscope contains a CCD sensor at the distal end of the device, which transmits a crystal-clear image of everything that happens during a surgery to a high-resolution medical monitor. It is one of the world’s most advanced developments in the sphere of medical equipment, far exceeding the performance of nephoscopes that transmit images to the camera via an optical fiber system, thus significantly limiting the image quality received by a urologist. Now physicians can more precisely visualize calculi and lead to them laser fiber of the desired diameter through the operating channel.
The CCD sensor is located on the tip of the flexible unit, which gives a perfect image and maximum flexibility
Cook Medical Rhapsody® H-30® Holmium Laser
This unit is a guarantee of reliable destruction of stone of any structure. The wave frequency and power output of the laser make it possible to set individual parameters for each particular concrement, since our task is not just to break up calculus, but to turn it into dust without damaging the surrounding tissues. To do this, we select the lowest pulse power, but deliver up to 20 beats per second using the thinnest fiber, thus sparing the surrounding tissue.
The range of fibers we operate is represented by all actual sizes: 0.2 mm, 0.275 mm, 0.375 mm, 0.550 mm, and 0.940 mm.
Of course, we should note the reliability of the laser and the products in general https://www.cookmedical.com/, which are gratefully used for medical treatment of patients all over the world. Our laser is a water-cooled unit with the largest radiator in its segment. It is a key parameter for sustainable operation of any laser, especially the one used for destruction of large and dense calculi.
A set of direct tools for work in bladder and ureter.
Our operating room offers a wide range of Karl Storz, Hawk, and Olimpus instruments of various length and diameter. A wide variety of tools and equipment is an extremely important in the endourology, as a urologist will always choose the thinnest possible tool for safe and successful surgery.
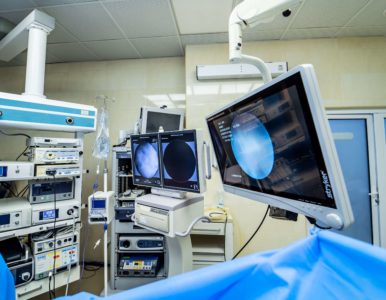
Display monitors and camera systems
For the best imaging during operations, we use medical Stryker and Olympus display monitors and camera systems, the most award-winning manufacturers in the industry, whose products allow us to obtain the highest quality images and to record the whole operation process, if necessary.
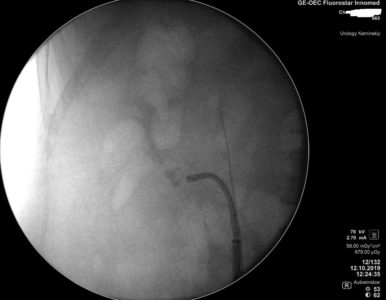
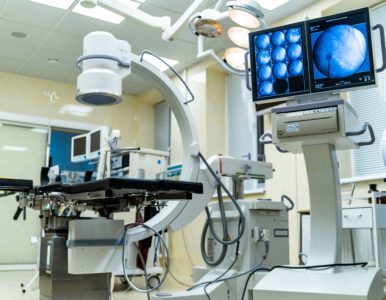
General Electric Fluorostar digital fluoroscope.
the body, we use a state-of-the-art Fluorostar digital fluoroscope produced by the American company General Electric.
This system is characterized by the highest image quality in its segment, which allows to ensure optimal level of safety for patients and surgeon`s team.
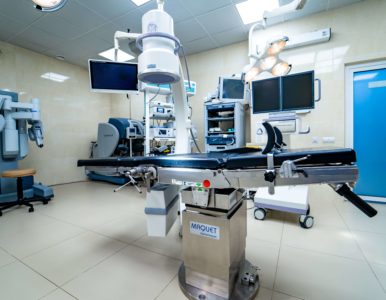
The Maquet operating table
The Maquet operating table makes it possible to quickly reposition a patient during surgery, which is extremely important for finding and destructing calculi and reliable control of fragments.
Of course, this is not a complete list of novel tools and accessories that we use to quickly and reliably destruct calculi in your kidneys and urethra.
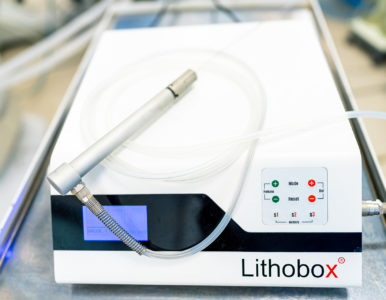
Pneumatic lithotripter
Among all the energies used for stone fragmentation in urology, pneumatic energy is the oldest. The principle of a pneumatic lithotripter is quite simple: a compressor delivers compressed air at a pressure of 3 to 8 bars into a cylinder, causing a metal piston inside to strike sharply against the base of a thin steel rod. The entire energy of the compressed air and the mass of the metal piston is concentrated at the tip of the rod, which is positioned close to the stone. This allows for a powerful impact on the stone, splitting it into fragments. This method is especially effective for stones with a large mass and density, whereas small stones easily fly away from the impact or absorb the energy if the stone has a soft structure. Therefore, the primary application of the pneumatic lithotripter is for large bladder and kidney stones. Typically, such stones are first fragmented pneumatically, and when it comes to smaller fragments, the laser takes over. This tandem allows for the rapid fragmentation of any stone and its removal from the kidney or bladder cavity. The advantages of the method are fully realized with a 5mm percutaneous access (mini PCNL), with a 1mm thick electrode. It is perfectly suited for our mini nephroscope. For the fragmentation of giant bladder stones, we can use thicker electrodes. Our modern pneumatic lithotripter allows adjusting the impact force from 3 to 8 bars and delivers from 3 to 15 strikes per second, which enables the selection of the ideal fragmentation mode for any stone.
Video of crushing a giant kidney stone using a pneumatic lithotripter
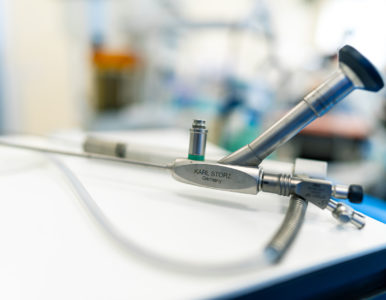
Mini nephroscope KARL STORZ
Percutaneous access is indeed a method that has been in use for many years. In Ukraine, the first percutaneous access to kidney stones was performed in 1992, and globally, it was much earlier. The main difficulty of such fragmentation was the kidney trauma inflicted during the operation and all the complications associated with it. However, the development of energies for stone fragmentation has made it possible to significantly reduce the diameter of the hole that needs to be made to reach the kidney stones. That is, if for many years the operation was called percutaneous (through the skin) nephrolithotripsy – PCNL, requiring a hole up to 10 mm in diameter, now the operation is called mini PCNL and requires just a 5 mm puncture. Accordingly, the instrument used for this intervention is called a mini nephroscope, and ours is from KARL STORZ. In terms of safety/result ratio, we consider this instrument to be the best.
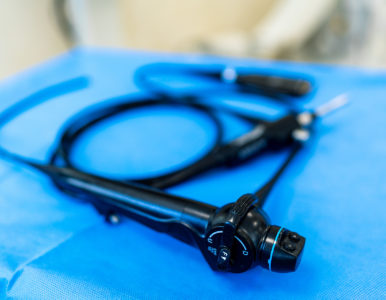
The Olympus CYF-V Flexible Video Cystoscope
It is a tool that allows the bladder to be inspected in all areas, even the most remote ones. This is particularly important when performing cystoscopy for the diagnosis of cancer or other additional bladder formations. Using a rigid (straight) cystoscope for this procedure leaves 10-20% of the bladder surface unexamined and carries the risk of an unreliable examination. Our instrument allows 100% of the bladder surface to be examined.
We also use this instrument for percutaneous stone fragmentation. By inserting the cystoscope through a puncture into the kidney, we gain access and the ability to fragment stones even in the most tortuous calyces. This approach protects our patients from additional punctures and reduces renal trauma.